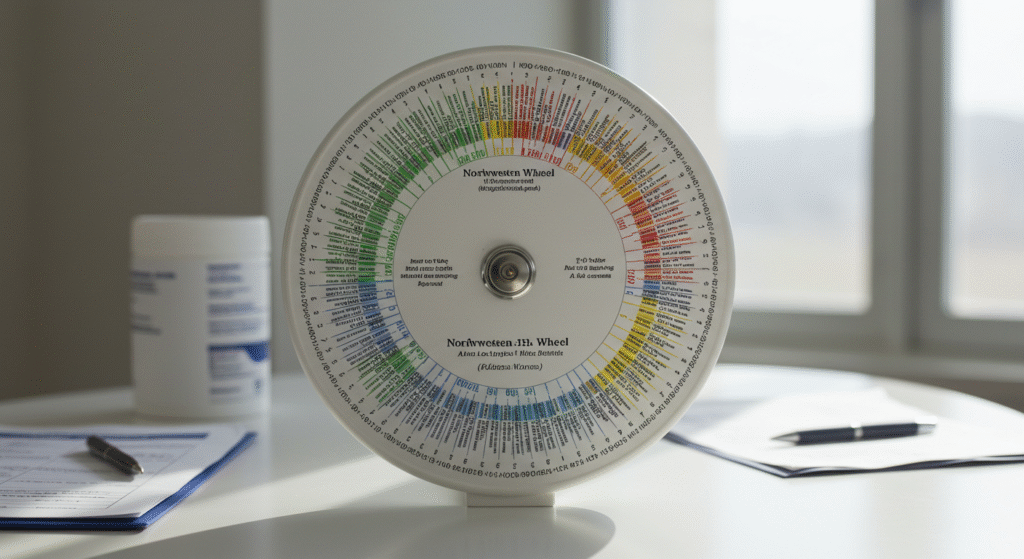
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel is an innovative clinical tool developed to simplify and optimize the selection of antibiotics in medical settings. As antimicrobial resistance becomes a growing global concern, tools that help healthcare providers make smart, evidence-based choices in real time are more important than ever. Designed by clinicians and educators at Northwestern University, this wheel provides an at-a-glance reference that groups antibiotics by their mechanisms of action, spectrum of activity, and clinical uses.
Unlike conventional antibiotic charts, which are often lengthy and text-heavy, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel is designed to be visually intuitive. It helps physicians, medical students, pharmacists, and other healthcare workers quickly identify the most appropriate antibiotic based on infection type, suspected organisms, and patient condition. The wheel is typically divided into colored zones or rings, each representing a particular class of antibiotic or bacterial target.
One of the standout features of the wheel is its versatility: it can be used in academic lectures, clinical rounds, and even bedside decision-making. With antibiotic misuse contributing heavily to resistance worldwide, tools like this represent a modern solution to a pressing issue. By merging visual learning with critical clinical decision-making, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel is a step forward in infectious disease education and treatment.
What Is the Purpose of the Antibiotic Wheel?
The primary purpose of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel is to assist healthcare professionals in selecting the most effective antibiotic therapy quickly and accurately. This tool acts as a decision-support aid that simplifies a traditionally complex process—matching infections to appropriate antimicrobial agents—into a structured, digestible visual format.
In clinical settings, doctors often face pressure to make rapid treatment decisions, especially in emergency rooms and critical care units. Without quick access to infectious disease consults or complete patient lab results, initial antibiotic choices are often empirical. The antibiotic wheel addresses this need by offering a systematic reference that includes key clinical factors: bacterial targets, antibiotic classes, resistance profiles, and potential side effects.
Furthermore, the wheel supports the overarching goal of antimicrobial stewardship—ensuring antibiotics are used appropriately to reduce resistance, side effects, and healthcare costs. It prevents unnecessary use of broad-spectrum antibiotics when a narrow-spectrum drug would suffice, thus promoting more responsible prescribing behavior.
Educationally, the wheel serves as a training resource for medical students and residents who are still learning the nuances of infectious diseases. It reinforces the connections between bacteria, drug classes, and indications in a memorable and practical way. In short, the purpose of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel is multifaceted: improving accuracy, promoting safety, educating learners, and fighting resistance.
History and Development at Northwestern University
The origins of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel trace back to the early 2010s when clinicians and educators at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine recognized a persistent challenge in antibiotic selection. Medical trainees often struggled to retain complex information about antimicrobial agents, and experienced providers faced time constraints that made reference-heavy charts inefficient. The solution was to design a compact, visual learning and clinical decision-making aid: the antibiotic wheel.
Initially conceptualized by infectious disease specialists and pharmacologists, the wheel underwent several rounds of development. The creators aimed to merge clarity with clinical depth—ensuring that each segment of the wheel reflected current evidence-based guidelines while remaining easy to interpret. Early versions were printed on laminated cards used during medical school instruction and hospital rounds.
As word spread, the wheel gained traction beyond Northwestern. Other institutions began adopting it as a teaching aid, and it was integrated into antimicrobial stewardship programs. Encouraged by the success, Northwestern refined the wheel further, introducing color coding, bacterial spectrum indicators, and guidance on first-line vs. second-line choices.
Over time, technological advancements enabled the wheel to go digital, allowing for interactive versions on tablets and hospital systems. Northwestern’s commitment to medical innovation has made this tool a staple in clinical education and practice, illustrating how academic institutions can lead meaningful change in healthcare delivery.
How the Antibiotic Wheel Works
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel functions as an intuitive visual guide that simplifies the complex decision-making involved in antibiotic prescribing. Structured like a circular chart, it typically consists of concentric rings and radial sectors, each designated for specific antibiotic classes and their bacterial targets. The wheel often employs a color-coded system, with different hues representing drug families such as beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, macrolides, and tetracyclines.
At the core of the wheel are bacterial categories: gram-positive, gram-negative, anaerobic, and atypical organisms. From the center outward, users can trace which antibiotics are most effective against which types of bacteria. This layered format allows for fast identification of effective agents for a given infection, such as pneumonia or urinary tract infections.
Each section of the wheel may also contain notes on drug toxicity, contraindications, or common resistance patterns. For example, the penicillin segment might include caveats about beta-lactamase-producing organisms. Similarly, the fluoroquinolone section might highlight risks like tendon rupture or QT prolongation.
The wheel can be used both as a printed reference card and in digital format. Interactive digital versions may include clickable segments, allowing clinicians to access deeper information like dosage, renal adjustment, and clinical indications. The wheel’s design encourages pattern recognition, helping users build a mental map of antibiotic choices that supports more efficient and safer prescribing.
Key Components of the Wheel
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel is composed of several critical components, each designed to support quick comprehension and clinical utility. These elements work together to create a highly functional visual guide, balancing simplicity with medical accuracy.
The first and most noticeable component is the color-coded segmentation. Each color represents a distinct class of antibiotics—penicillins might be blue, macrolides red, cephalosporins green, etc. This color-coding enhances visual memory and allows for rapid categorization during use.
Next are the concentric rings and radial arms that form the wheel’s structure. The innermost rings often represent broader-spectrum antibiotics, while outer rings may list narrow-spectrum or highly specialized agents. This organization reflects the hierarchy of antibiotic escalation, a concept central to antimicrobial stewardship.
Another crucial component is the bacterial spectrum index, which maps each antibiotic to its likely effective bacterial targets—such as gram-positive cocci, gram-negative rods, anaerobes, or atypical organisms. This helps clinicians understand not only what an antibiotic does, but what it shouldn’t be used for, reducing misuse.
In many versions, icons or legends are included to indicate important clinical factors like renal dosing, black-box warnings, or pregnancy safety. The wheel may also reference first-line vs. second-line choices for specific infections.
Collectively, these components make the wheel more than just a reference chart; they turn it into a multidimensional tool for smart, responsive clinical decision-making.
Classes of Antibiotics Represented
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel includes a wide range of antibiotic classes, making it a comprehensive visual reference for nearly all commonly used antimicrobial agents. Each class is carefully placed on the wheel based on its spectrum of activity, target organisms, and typical clinical use. This layout allows healthcare providers to quickly compare classes when choosing appropriate therapy.
Among the core antibiotic classes featured are penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams—all of which fall under the beta-lactam category. These are generally indicated for a wide range of infections, from skin and soft tissue to respiratory and urinary tract infections. Each subclass—such as first, second, or third-generation cephalosporins—is often displayed in a separate section to highlight its specific applications.
Macrolides and tetracyclines are also well represented, known for their effectiveness against atypical pathogens and upper respiratory infections. Aminoglycosides, typically reserved for gram-negative infections, are positioned to indicate their strong bactericidal properties but also include cautionary notes regarding nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity.
Fluoroquinolones, glycopeptides (such as vancomycin), and lincosamides (like clindamycin) appear with special markings due to their side-effect profiles or resistance concerns. Lastly, less frequently used but clinically important classes such as oxazolidinones (linezolid) and polymyxins are also included to support nuanced prescribing decisions in complex or resistant infections.
By organizing antibiotics into distinct classes with clear visuals and color-coded zones, the wheel enhances clinical reasoning and helps practitioners avoid inappropriate overlaps or unnecessary broad-spectrum coverage.
How Physicians Use the Antibiotic Wheel
Physicians utilize the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel as a practical decision-making tool during clinical evaluations, especially in environments where rapid choices are necessary. Whether on hospital rounds, in emergency departments, or during inpatient consults, the wheel offers a real-time reference to guide antibiotic therapy based on infection type, suspected pathogens, and patient-specific factors.
When a patient presents with signs of infection, the physician can consult the wheel to identify which antibiotic class is most appropriate for the condition at hand. For example, if the infection appears to be caused by gram-negative rods, the physician can easily scan the wheel for antibiotics with high gram-negative coverage. The wheel’s structure allows a direct visual comparison of spectrum, side effects, and potential interactions.
In some versions, physicians may also use the wheel to cross-reference antibiotic resistance data. If local antibiograms indicate high resistance to a certain drug in community-acquired infections, the wheel helps in selecting an alternative with a better resistance profile. Furthermore, physicians teaching students or residents often use the wheel as an educational prop to explain rationale behind drug selection.
Some hospitals integrate the wheel into digital systems like electronic health records (EHRs) or antimicrobial stewardship platforms, further enhancing its accessibility. The wheel saves time, supports accuracy, and helps physicians strike the right balance between efficacy and safety in antimicrobial prescribing.
Educational Value for Medical Students
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel is not just a clinical tool—it’s a powerful educational resource for medical students and residents. Learning about antibiotics can be daunting due to the vast number of drug classes, resistance mechanisms, and clinical guidelines. The wheel simplifies this learning process by organizing information visually and logically.
Medical students often struggle with memorizing long lists of antibiotics and their bacterial targets. The wheel mitigates this by showing relationships between drug classes and organisms in a visual framework. This aids memory retention, allowing students to understand the big picture rather than relying solely on rote memorization.
Additionally, the wheel supports active learning. In classroom or bedside teaching, instructors may pose clinical scenarios and ask students to use the wheel to identify appropriate antibiotics. This interactive approach reinforces theoretical knowledge with real-world applications, promoting critical thinking.
Because the wheel integrates core pharmacological concepts—like spectrum of activity, side effects, and indications—it provides a multidimensional learning experience. Students not only learn which antibiotics to use, but why certain choices are better for specific cases. This prepares them for responsible prescribing in their future careers.
In essence, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel bridges the gap between theory and practice, empowering medical learners to gain confidence in antimicrobial selection while developing strong clinical judgment.
Integration into Clinical Practice
The integration of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel into clinical practice has significantly improved how healthcare professionals manage infectious diseases. Many hospitals, especially those affiliated with academic institutions like Northwestern, incorporate the wheel into their treatment protocols and daily rounds. Its utility in streamlining antibiotic selection makes it an essential tool for busy clinical environments.
Typically, the wheel is made available in both print and digital forms. Printed versions are laminated and kept in consultation rooms or carried by residents during rounds. Meanwhile, digital versions are integrated into hospital intranet systems or clinical decision support software, allowing easy access via desktops, tablets, or even smartphones. These digital formats may include interactive features, such as clicking on a drug name to view dosing, side effects, and contraindications.
Antimicrobial stewardship teams often use the wheel to guide policy-making and monitor antibiotic use patterns across departments. By ensuring that prescribers follow evidence-based guidelines, the wheel reduces inappropriate prescriptions, lowers resistance rates, and improves patient safety.
Pharmacists also rely on the wheel when reviewing antibiotic orders, checking for duplications, and recommending safer alternatives. In multidisciplinary rounds, having a unified visual reference ensures that doctors, pharmacists, and nurses are on the same page.
Ultimately, the wheel’s integration leads to faster decisions, fewer errors, and more effective infection management, aligning with the best practices of modern healthcare delivery.
Benefits Over Traditional Antibiotic Charts
Compared to traditional antibiotic reference charts, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel offers several practical and educational advantages that make it a superior tool for many users. The primary benefit lies in its visual design, which provides a more intuitive and user-friendly layout. Instead of scrolling through pages of tabular data, users can visually scan the wheel to identify relevant antibiotic options, saving valuable time in high-pressure situations.
Another key benefit is the wheel’s ability to illustrate relationships between drug classes, bacterial targets, and clinical scenarios. Traditional charts often separate antibiotics by class or infection type, making it difficult to cross-reference effectively. The wheel, on the other hand, combines these factors in one integrated graphic, helping users understand the full context of antimicrobial selection.
The wheel also enhances learning and retention. For students and junior physicians, complex pharmacologic information is more accessible when presented visually. Many users find that they can recall the wheel’s layout during exams or patient care discussions, reinforcing the value of visual memory.
From a usability perspective, the wheel is compact and portable. It can be printed on a pocket card or accessed digitally on mobile devices, making it more convenient than bulky textbooks or web-based databases.
Finally, by promoting faster, more accurate decision-making and reducing the risk of broad-spectrum antibiotic overuse, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel contributes to better patient outcomes and stronger antimicrobial stewardship efforts.
Visual Design and User Interface
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel’s visual design and user interface are integral to its effectiveness. It was crafted with the goal of simplifying a complex medical domain through smart use of layout, color, and symbols. Unlike text-heavy drug databases or dense pharmacology books, the wheel presents information in a spatial, color-coded format that allows for fast recognition and retrieval of key facts. This makes it a particularly valuable tool during time-sensitive clinical decision-making.
The circular format of the wheel symbolizes the interconnected nature of antibiotic therapy. In the center are core infection types or bacterial groups, while the outer segments represent classes of antibiotics suited to treat those conditions. The radial layout naturally guides the user’s eye outward from the diagnosis to possible treatments. Each segment is labeled with the antibiotic class, examples of specific drugs, and common usage notes or warnings.
Color schemes are not just decorative—they indicate activity spectrum, toxicity levels, or antibiotic stewardship preference (first-line vs. reserve antibiotics). Symbols or icons may denote whether an agent requires renal dose adjustment, is contraindicated in pregnancy, or is known for high resistance rates.
Digital versions of the wheel elevate the interface further by adding interactive elements. Clickable areas offer deeper information, and some even include real-time updates aligned with new guidelines or hospital antibiograms. The interface is optimized for both desktop and mobile use, ensuring that whether at the bedside or in a classroom, the tool remains practical and user-friendly.
How the Wheel Helps Prevent Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance is one of the most pressing global health threats of the 21st century, and the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel plays a direct role in combating this crisis. By guiding clinicians toward the most appropriate and narrow-spectrum antibiotics for specific infections, the wheel significantly reduces the misuse and overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics—one of the main drivers of resistance.
When healthcare providers use the wheel, they are less likely to resort to empirical therapy with broad-spectrum agents, especially in situations where targeted options are available. For instance, the wheel visually shows when a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam would suffice instead of prescribing a fluoroquinolone or carbapenem. This selective approach ensures that more powerful antibiotics are reserved for cases that truly need them.
Moreover, the wheel supports antimicrobial stewardship initiatives by aligning with institutional protocols. It encourages best practices such as de-escalation of therapy once culture results are available, time-limited prescriptions, and monitoring for drug interactions or side effects. These strategies are critical in preserving the efficacy of existing antibiotics and extending their lifespan.
In educational settings, the wheel teaches new clinicians to think critically about antimicrobial choices, reinforcing habits that prioritize precision over convenience. By institutionalizing this tool, hospitals contribute to global efforts to slow down resistance and ensure antibiotics remain effective for future generations.
Case Studies and Real-Life Applications
The effectiveness of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel becomes most apparent when observed through real-life case studies and clinical applications. Numerous medical institutions have documented the benefits of integrating the wheel into routine patient care, ranging from improved prescribing accuracy to reduced infection-related complications.
For example, a teaching hospital in Chicago implemented the wheel during their internal medicine rotation for residents. During rounds, the medical team used the wheel to discuss the best empirical antibiotics for various patient presentations. One case involved a patient with community-acquired pneumonia. Instead of immediately prescribing a broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone, the team referred to the wheel and selected a targeted macrolide combined with a beta-lactam—an equally effective yet more stewardship-aligned choice. The patient recovered without complications, and the stewardship committee flagged this as a best-practice case.
Another case at a rural hospital demonstrated how the wheel could guide urgent care physicians without infectious disease backup. A child presented with a complicated urinary tract infection. With limited lab data initially available, the physician used the wheel to choose a narrow-spectrum cephalosporin appropriate for pediatric care. Later, the culture confirmed E. coli sensitive to the selected agent.
These case studies highlight the wheel’s role not just as a reference, but as a real-world decision aid that leads to better outcomes, improved patient safety, and smarter use of antibiotics.
Digital vs Physical Formats of the Wheel
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel is available in both digital and physical formats, each offering unique advantages depending on the clinical environment and user preference. The physical version typically consists of a laminated card or rotating paper disc that medical professionals can carry in their lab coats or attach to clipboards. Its portability and simplicity make it ideal for quick references during bedside rounds, teaching sessions, or in outpatient clinics with limited digital infrastructure.
However, the digital format is increasingly favored in modern hospital systems due to its dynamic and interactive features. These versions are often embedded in electronic health record (EHR) platforms, medical apps, or online portals, allowing users to access expanded content with a few taps or clicks. Digital wheels may provide additional layers of information, such as updated antibiogram data, clinical guidelines from organizations like the CDC or WHO, and tailored dosing recommendations based on renal function or patient weight.
The digital version can also include alerts for drug allergies, black box warnings, and contraindications, helping reduce prescription errors. Some institutions even customize the digital wheel to reflect local resistance trends, creating a localized antibiotic strategy that strengthens stewardship programs.
In essence, while the physical version offers tactile convenience and quick scanning, the digital version enhances depth, personalization, and real-time adaptability. Many practitioners find value in using both formats side-by-side for an optimal clinical experience.
Role in Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs
Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) are designed to promote the appropriate use of antibiotics, improve patient outcomes, and curb the development of resistance. The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel has become a central element in many of these programs, especially in academic and teaching hospitals. It empowers healthcare teams with an evidence-based, easy-to-use tool that supports precise antibiotic prescribing aligned with stewardship principles.
The wheel aids in standardizing treatment across departments by acting as a reference guide that clinicians can universally follow. This uniformity is crucial in maintaining consistency in antibiotic use, particularly for commonly encountered infections such as urinary tract infections, pneumonia, cellulitis, or sepsis. It ensures that patients receive antibiotics that are not only clinically effective but also carry the least risk for promoting resistance.
Stewardship committees often use the wheel during prescription audits and feedback sessions. When reviewing antibiotic usage data, they can cross-reference whether physicians followed wheel-based recommendations, helping identify areas for training or adjustment.
Furthermore, educational seminars on stewardship frequently feature the wheel as a visual anchor for presentations and workshops. Its graphic representation of appropriate antibiotic use makes complex information digestible, encouraging buy-in from multidisciplinary teams including doctors, pharmacists, nurses, and administrators.
By integrating the wheel into ASPs, hospitals reinforce responsible prescribing habits and align with national and global goals for sustainable antibiotic use.
Limitations and Areas for Improvement
While the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel offers many advantages in clinical practice and education, it is not without limitations. One of the primary concerns is that the wheel, like any reference tool, can become outdated if not regularly updated. Antibiotic resistance patterns change over time, and newly developed antibiotics or revised treatment guidelines may not be immediately reflected in older versions of the wheel. This can result in physicians using outdated information if they rely solely on a static wheel without verifying against current clinical data.
Another limitation lies in its generalization. The wheel often provides a broad overview of drug classes and spectrums but may lack the granularity needed for certain clinical scenarios. For example, it may not account for site-specific pharmacokinetics, drug penetration at infection sites, or patient-specific variables like immunocompromised status or allergies.
Additionally, the visual format, while intuitive, may oversimplify the complexities of antibiotic decision-making. Some users may interpret the wheel as a substitute for clinical judgment rather than a complementary tool. This could lead to over-reliance and inappropriate prescriptions in nuanced cases.
Areas for improvement include incorporating machine learning algorithms for real-time updates, expanding interaction with local antibiogram data, and enhancing the depth of information in digital formats. Improved multilingual versions and versions tailored for pediatric or geriatric populations could also broaden its usefulness across global healthcare settings.
Comparison With Other Antibiotic Selection Tools
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel stands out among antibiotic selection tools due to its unique visual approach, but it’s worth comparing it to other popular systems to appreciate its specific strengths and limitations. Traditional tools include printed antibiotic formularies, decision-making flowcharts, smartphone apps, and comprehensive databases like UpToDate, Epocrates, or Sanford Guide.
Whereas the Northwestern Wheel presents information visually and compactly, tools like UpToDate offer deeply detailed and continuously updated articles. However, those platforms may require more time and effort to navigate, making them less efficient in fast-paced environments like emergency departments or ICUs. In contrast, the wheel provides a quick reference that can be used during rounds or bedside discussions with minimal distraction.
Mobile apps offer the advantage of interactive guidance and up-to-date clinical data, similar to digital versions of the antibiotic wheel. However, these apps may have learning curves, depend on internet access, and sometimes overwhelm users with excessive options or technical language. The wheel’s simplicity offers a refreshing balance by focusing on core prescribing principles, especially for students or junior doctors.
Other tools like antibiogram-based local hospital charts are useful for resistance tracking but often lack the ease-of-use or visual appeal of the wheel. By combining accessibility, visual clarity, and practical application, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel remains a preferred quick-reference tool, particularly in educational and early-career clinical environments.
Patient Safety and Clinical Accuracy
Patient safety is a cornerstone of effective healthcare delivery, and the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel plays a vital role in ensuring accurate, safe, and timely treatment decisions. By visually aligning the most appropriate antibiotic choices with specific infections and bacterial targets, the wheel minimizes the risk of prescription errors that can lead to harmful outcomes.
One of the major ways the wheel enhances patient safety is by discouraging the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics. This not only prevents unnecessary side effects like C. difficile infections or allergic reactions but also reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance, which is a major threat to future treatment options. The wheel’s emphasis on choosing narrow-spectrum agents when appropriate promotes individualized therapy tailored to each patient’s condition.
Moreover, the wheel helps clinicians avoid commonly known drug interactions and contraindications. For instance, certain segments of the wheel highlight agents that require renal dose adjustments or that are unsafe during pregnancy. This visual cue system provides clinicians with real-time safety reminders, even in busy hospital environments.
By simplifying and systematizing the antibiotic selection process, the wheel reduces variability in treatment approaches across providers and departments. Standardization itself contributes to safety by minimizing reliance on memory or inconsistent guidelines. Overall, the wheel acts as a valuable guardrail against error, making antibiotic prescribing safer and more effective.
Research Studies on Wheel Effectiveness
Several research studies and institutional evaluations have examined the impact of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel on clinical outcomes, education, and prescribing behavior. These studies have generally shown favorable results, supporting the wheel’s continued use and development in healthcare environments.
At Northwestern University Medical Center, an internal study involving medical students and residents demonstrated a measurable improvement in antimicrobial selection accuracy after integrating the wheel into daily teaching rounds. The learners not only retained knowledge better but also expressed increased confidence in their ability to select appropriate empirical therapy for common infections.
Another study at a regional hospital in the Midwest compared antibiotic prescribing practices before and after the introduction of the wheel. The data revealed a significant reduction in unnecessary broad-spectrum prescriptions and an increase in guideline-adherent therapy. This resulted in a lower incidence of hospital-acquired infections, shorter hospital stays, and improved antimicrobial stewardship metrics.
Additional surveys conducted in pharmacy departments indicated that clinicians found the wheel helpful in streamlining interdepartmental consultations and dose adjustments. Pharmacists reported that it served as a communication bridge between prescribers and stewardship teams, improving patient management.
These research outcomes collectively validate the clinical relevance and educational value of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel. They also encourage broader implementation, especially in teaching institutions and community hospitals where quick, reliable antibiotic selection tools are essential.
Feedback from Healthcare Professionals
Feedback from healthcare professionals who use the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel has been overwhelmingly positive, particularly in the areas of usability, efficiency, and educational utility. Physicians across various specialties—including internal medicine, pediatrics, surgery, and emergency medicine—have praised the tool for its simplicity and accessibility during high-pressure clinical situations.
Residents and medical students often comment on how the wheel helped them bridge the gap between theoretical pharmacology and real-world prescribing. Many cite it as their go-to reference during inpatient rotations, noting that its visual layout helped them internalize core concepts more effectively than traditional drug lists or textbooks.
Pharmacists have also found the wheel useful during medication reconciliation and chart reviews. They frequently rely on it when cross-checking prescriptions and making recommendations for dose adjustments or alternative therapies. The wheel aids in promoting consistent language and understanding between pharmacists and prescribing physicians, leading to fewer prescription errors.
Even nurse practitioners and physician assistants report using the wheel for patient education and consultation. For example, when explaining why a specific antibiotic is preferred over another, the visual aid helps clarify concepts for patients and caregivers.
In institutional surveys, healthcare providers consistently rate the wheel high for clarity, practical relevance, and its role in promoting safer prescribing habits. Suggestions for future improvement include more disease-specific overlays, real-time integration with EHRs, and mobile-app functionality.
Customization for Specific Medical Fields
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel has shown great potential for customization to suit the specific needs of various medical specialties. While its core structure is useful across general medicine, tailoring the content to match specialty-specific infections, pathogens, and drug considerations enhances its functionality and relevance in specialized fields.
In infectious disease (ID) departments, the wheel can include advanced antibiotic options like daptomycin, colistin, or linezolid, used in complex infections or multidrug-resistant cases. These additions help specialists make nuanced decisions during consultations, especially for patients with comorbidities or immune suppression.
In pediatrics, modifications to the wheel might include weight-based dosing guidance, pediatric-specific infection considerations like otitis media or group B strep, and a clearer delineation of safe versus contraindicated drugs in children. Similarly, OB/GYN departments could benefit from versions that focus on drugs safe for use during pregnancy or lactation, as well as treatment options for common infections like UTIs or bacterial vaginosis.
Surgical departments might request customization that prioritizes perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis guidelines and post-operative infection management. Orthopedics and trauma surgery, in particular, could use additions related to bone and joint infections.
These specialty-specific versions preserve the visual strengths of the original wheel while adding practical layers relevant to each clinical focus. The flexibility to adjust the wheel’s design without compromising its clarity makes it a powerful tool across diverse branches of medicine.
Use in Global Healthcare Settings
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel holds valuable promise for improving antibiotic prescribing in global healthcare settings, especially in low- and middle-income countries where access to infectious disease specialists and up-to-date prescribing resources may be limited. Its compact, visual format and ease of use make it particularly well-suited to environments where clinical decisions need to be made swiftly and often without digital infrastructure.
In resource-limited hospitals and rural clinics, printed versions of the wheel can act as a key reference for general practitioners, nurses, and health officers. Since these providers often treat a wide range of infections with limited drug availability, a simplified guide to choosing appropriate and locally effective antibiotics can significantly reduce misprescribing.
International health organizations have expressed interest in adapting the wheel to reflect regional resistance trends, prevalent pathogens, and the local antibiotic formulary. For instance, in Southeast Asia, tuberculosis and typhoid-specific options might be included, whereas in parts of Africa, the wheel may prioritize malaria co-infections or HIV-related infections.
Additionally, translation into local languages and pictorial enhancements could help overcome language and literacy barriers, ensuring accessibility for healthcare workers at all levels of training.
In humanitarian aid and disaster response scenarios, laminated wheels can be distributed as part of medical kits, providing essential guidance for emergency antibiotic use. Overall, the wheel offers an affordable, scalable, and adaptable solution to global antibiotic management challenges.
Future Updates and Innovations
As the field of infectious diseases continues to evolve, future updates and innovations to the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel will be crucial to maintaining its clinical relevance and effectiveness. The integration of artificial intelligence and real-time data inputs is one of the most exciting directions for the next generation of this tool.
One anticipated improvement is the development of dynamic digital versions that can sync with hospital antibiograms, updating bacterial resistance trends in real time. This would allow clinicians to see which antibiotics are most effective in their facility based on the latest lab data, making the wheel more than a static reference—transforming it into a smart decision engine.
Additionally, integration with EHR systems could allow the wheel to automatically suggest antibiotics based on patient history, allergies, renal function, and microbiology results. These intelligent features would reduce the cognitive load on clinicians and help standardize antibiotic use across institutions.
Another potential innovation involves expanding the wheel’s functionality through augmented reality (AR). Medical trainees could use AR apps to explore the wheel in 3D, deepening their understanding through interactive educational modules, case scenarios, and quizzes.
User feedback and open-source collaboration may also lead to specialized wheels tailored to different countries, patient demographics, and infection types. The future of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel lies in its ability to evolve with medicine itself—maintaining its user-friendly format while expanding its depth and technological integration.
Integration With Mobile Health Apps
Mobile health (mHealth) technology is reshaping the way healthcare is delivered and accessed, and the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel has begun making its mark within this movement through integration with medical mobile applications. These digital enhancements make the wheel more accessible, interactive, and responsive to clinicians’ needs at the point of care.
A mobile-integrated version of the wheel typically includes touch-based navigation that lets users select a drug class or infection type and view recommendations instantly. Features such as voice search, dosage calculators, and side-effect alerts make the app even more functional for busy healthcare providers. Some versions allow users to input patient-specific factors such as allergies, weight, or kidney function to customize antibiotic recommendations.
App-based versions can also notify users of important updates, such as new antibiotic approvals or changes in resistance data. In hospital settings, integration with mobile-friendly electronic medical records enables seamless documentation and ordering based on wheel-based selections.
Students and residents benefit significantly from mobile integration by being able to carry a full antibiotic reference tool in their pocket, ready for use during rounds, exams, or discussions. Offline access is also critical for rural clinics or areas with limited internet connectivity.
Ultimately, by expanding into the mHealth space, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel becomes a living, learning, and prescribing companion—bridging the gap between knowledge and action in real time.
Role in Pandemic Preparedness and Response
During global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, tools such as the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel have proven especially valuable in maintaining safe and effective antibiotic use under challenging conditions. While COVID-19 is a viral illness, many patients hospitalized with it developed secondary bacterial infections, leading to increased antibiotic prescribing—often empirically and without full diagnostic clarity.
The wheel helped healthcare providers stay grounded in rational prescribing principles even amid uncertainty. By providing a structured way to evaluate which antibiotics were necessary and which were not, the wheel supported antimicrobial stewardship goals at a time when overprescribing risks were particularly high.
In overwhelmed healthcare systems where staffing shortages and patient surges stressed clinical judgment, the wheel acted as a quick and reliable decision-making aid. It ensured that newer or redeployed staff could still access guidance aligned with institutional standards. In field hospitals and makeshift ICUs, printed wheels allowed clinicians to make consistent decisions even in the absence of advanced technology or specialist consults.
Looking forward, pandemic preparedness plans may include the distribution of customized wheels tailored to likely co-infections or complications associated with future viral outbreaks. The wheel could also serve as a teaching and triage tool in outbreak response training, helping healthcare workers respond confidently and consistently.
By supporting responsible antibiotic use in the midst of chaos, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel proves itself not just a clinical tool—but a pillar of healthcare resilience.
Training and Certification Use
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel has become a valuable component in medical training and certification processes. It is frequently used in workshops, board review sessions, and continuing medical education (CME) courses to reinforce rational prescribing practices among medical students, residents, and practicing clinicians.
During internal medicine and infectious disease rotations, instructors often rely on the wheel to simulate real-world scenarios. Trainees are asked to reference the wheel to select empiric and targeted therapies, identify potential drug interactions, and recognize when to escalate or de-escalate treatment. This not only builds confidence but ensures that prescribing habits are grounded in evidence-based guidelines.
Some residency programs have formally included the wheel in their assessments. For example, examiners may present infection cases and require candidates to use the wheel to justify their antibiotic choices. The visual nature of the wheel helps participants articulate their thought processes, making it easier to evaluate both their clinical reasoning and their understanding of antimicrobial principles.
In certification courses for nurse practitioners and physician assistants, the wheel serves as a key teaching tool. It reduces reliance on memorization by promoting understanding of antibiotic classes and resistance risks. As training institutions recognize its value, the wheel continues to establish itself as a benchmark of competence in antimicrobial stewardship and safe prescribing.
Contributions to Public Health Awareness
Beyond clinical and academic environments, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel also contributes to public health awareness about responsible antibiotic use. As antimicrobial resistance becomes an increasingly urgent global issue, tools that support both education and outreach are essential. The wheel offers an accessible visual representation of antibiotic principles that can be shared with patients, caregivers, and the wider public.
Public health campaigns often struggle to communicate the dangers of antibiotic misuse. The wheel can serve as a communication aid in clinics, pharmacies, and community health centers to show how antibiotics work and why not all infections require them. For example, providers can use it to explain why a cold or flu doesn’t need antibiotics, or why completing the prescribed course is essential—even if symptoms improve early.
Some institutions have adapted simplified versions of the wheel specifically for patient education. These versions use more visuals and layman-friendly language to depict how antibiotic overuse can lead to resistance, superbugs, and treatment failure. This helps demystify the science for non-clinical audiences.
By encouraging dialogue between providers and patients, the wheel fosters shared responsibility in infection management. It empowers patients to ask informed questions and adhere to recommendations, ultimately strengthening the public health response to the antibiotic resistance crisis.
Collaboration With Pharmaceutical Research
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel has begun to attract attention from pharmaceutical researchers and drug developers as a potential tool for guiding product positioning, clinical trials, and post-market education. Its ability to map out the spectrum and classification of existing antibiotics provides a useful framework for identifying gaps in current treatment options—gaps that new drugs might aim to fill.
Pharmaceutical companies developing novel antibiotics can use the wheel format to demonstrate how their new agent compares with existing drugs. For instance, if a company is launching an antibiotic effective against resistant gram-negative pathogens, they can illustrate its placement in relation to carbapenems, polymyxins, or aminoglycosides on the wheel. This helps clinicians quickly understand where the new agent fits in the therapeutic arsenal.
In clinical trials, researchers can refer to the wheel to ensure balanced comparator studies, selecting antibiotics from the same class or with overlapping spectrums. This visual strategy supports more transparent and comprehensible study designs, especially when communicating with regulatory bodies or advisory panels.
Post-approval, pharmaceutical teams have begun creating branded versions of the wheel to support physician education and product awareness. These collaborations demonstrate the wheel’s versatility—not only as a clinical guide but as a strategic tool in antibiotic research, innovation, and dissemination.
User Testimonials and Real-World Feedback
User testimonials from diverse healthcare professionals offer powerful validation of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel’s impact in real-world practice. Physicians, pharmacists, nurse practitioners, and medical educators across institutions have shared how this tool improves their day-to-day workflow, enhances their confidence in decision-making, and reinforces safe prescribing behavior.
A resident physician from a teaching hospital in New York shared that the wheel helped them reduce reliance on guesswork when faced with new cases. Instead of flipping through apps or outdated printouts, the wheel offered a quick, clear overview of viable antibiotic options tailored to each case. They appreciated its balance between brevity and substance.
Pharmacists have reported that the wheel streamlines their consultations with physicians during inpatient reviews. One ICU pharmacist mentioned how the wheel’s layout helped bridge communication gaps with junior staff who were unsure about escalation paths for resistant infections. The wheel functioned as a mutual reference point during decision-making.
Nurse practitioners working in outpatient clinics say that the wheel gives them confidence when treating infections without immediate specialist input. It helps them avoid unnecessary broad-spectrum drugs and provides solid talking points when counseling patients about prescription decisions.
Overall, real-world feedback reinforces that the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel is more than a visual aid—it’s a trusted tool that blends science, efficiency, and communication across every tier of healthcare.
Long-Term Impact on Medical Practice
The long-term impact of the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel on medical practice extends beyond the clinical floor into broader cultural shifts in how antibiotics are understood, prescribed, and taught. As more institutions adopt this tool, it is gradually becoming part of the standard toolkit for responsible antimicrobial management.
Its inclusion in medical curricula, continuing education, and stewardship protocols ensures that new generations of healthcare providers are trained with visual, systems-based thinking. This approach fosters a more intuitive understanding of microbial coverage, resistance mechanisms, and pharmacodynamics—concepts that are foundational to safe and effective prescribing.
Over time, widespread use of the wheel may lead to measurable reductions in inappropriate antibiotic use, lower hospital resistance rates, and fewer medication errors. It also contributes to standardizing antimicrobial decision-making across facilities, which supports consistency in treatment outcomes and data collection for public health monitoring.
In the broader scope, the wheel encourages a culture of accountability and education. Its influence spreads from the prescribing desk to the patient’s understanding, helping build a healthcare environment where antibiotics are used wisely, sparingly, and precisely.
As the healthcare community continues to adapt to emerging pathogens and evolving resistance patterns, the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel will likely remain a central element in shaping informed, data-driven, and patient-centered medical practice.
Conclusion
The Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel stands as a revolutionary tool in modern medicine, offering a visually intuitive, educationally powerful, and clinically practical approach to antibiotic selection. By bridging the gap between pharmacological complexity and clinical usability, the wheel supports improved prescribing, safer patient outcomes, and stronger antimicrobial stewardship. Whether used by seasoned physicians, medical students, or global health workers, the wheel continues to redefine how antibiotics are understood and applied across healthcare systems. Its adaptability, user-centered design, and impact on both education and clinical practice make it an enduring asset in the fight against antibiotic resistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the Northwestern Antibiotic Wheel used for?
It is used by healthcare professionals to select the most appropriate antibiotic based on infection type, resistance patterns, and drug class.
2. Is the antibiotic wheel only for doctors?
No, it’s used by a wide range of professionals including pharmacists, nurse practitioners, students, and public health educators.
3. How does the wheel support antimicrobial stewardship?
It promotes narrow-spectrum antibiotic use, reduces overprescription, and aligns treatment with evidence-based guidelines.
4. Can the wheel be used in countries outside the U.S.?
Yes, and it can be customized to reflect regional pathogens, language needs, and available antibiotics.
5. Is there a digital or app version of the wheel available?
Yes, many hospitals and institutions use interactive digital versions, and some are integrated into mobile health apps for easier access.
Let me know if you’d like a one-image visual prompt based on this article’s concept or a downloadable version for reference.