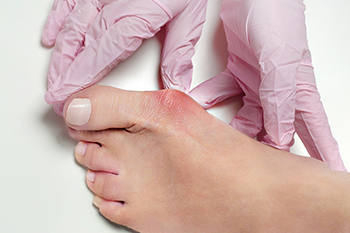
A bunion develops when the joint at the base of your big toe becomes misaligned, causing the bone to jut outward. The result is discomfort, swelling, and difficulty fitting into shoes. Severe bunions can lead to chronic pain, limited mobility, and complications like arthritis in the affected joint. For some, managing this condition with non-invasive methods works. Here’s what may be recommended for more serious cases:
When is Surgery Necessary?
Non-surgical treatments are typically the first step in treating bunions. These include wearing orthotic shoes, using pain relief medications, and receiving steroid injections to help manage symptoms. If these treatments do not relieve pain or restore mobility, surgery may be the next option. This surgery is designed to reduce pain, correct joint alignment, and enable patients to return to their normal activities without ongoing discomfort. The following types of surgery may be recommended:
Bunionectomy
For moderate to severe bunion cases, bunionectomy is usually recommended. This procedure involves removing the bulging part of the bone and realigning the joint. It’s effective for reducing pain and restoring proper alignment without being overly complex.
Osteotomy
An osteotomy involves cutting and repositioning the bone. Surgeons make precise cuts and then secure the bone in the correct position using screws or pins. This method addresses the structural deformity directly, making it ideal for severe cases where the toe joint is badly misaligned.
Arthrodesis
When arthritis has severely damaged the joint, arthrodesis may be the best option. This procedure permanently fuses the joint. It helps by eliminating pain but also limiting movement. It is typically reserved for patients who have tried other options without success.
Exostectomy
For less severe pain and mobility issues, exostectomy might be suitable. The procedure involves removing only the bunion itself without changing the alignment of the bone. Although less invasive, it can be combined with other surgeries for more lasting results.
Lapidus
The Lapidus procedure focuses on stabilizing the joint at the base of the bunion. It involves fusing the unstable joint to improve alignment. This surgery is particularly effective for individuals with hypermobility-related bunions or those who have experienced recurrent issues following previous surgeries.
What Happens After Surgery?
Surgery is only the first step toward recovery. After the procedure, proper post-operative care supports healing and helps you regain mobility. Here’s what typically follows a bunion surgery:
- Initial Rest: Patients are advised to stay off their feet for a few days. Elevating the foot reduces swelling during the initial recovery phase.
- Protective Footwear: Special post-operative shoes stabilize the foot while allowing for limited movement.
- Helpful Exercises: Gentle physical therapy strengthens the foot and restores flexibility.
- Increased Activities: Walking and daily activities resume gradually, with many patients fully recovering within 6-8 weeks, depending on the procedure.
Adhering to your doctor’s recovery plan speeds up healing and reduces complications.
Find a Foot Doctor for Bunion Removal
Living with severe bunions is not just about enduring discomfort. Knowing the available surgical options helps you make informed choices for lasting relief. Whether you explore minimally invasive methods or more involved procedures, the path toward recovery starts with expert guidance. Consulting a foot specialist ensures that your treatment plan matches your specific condition and lifestyle.