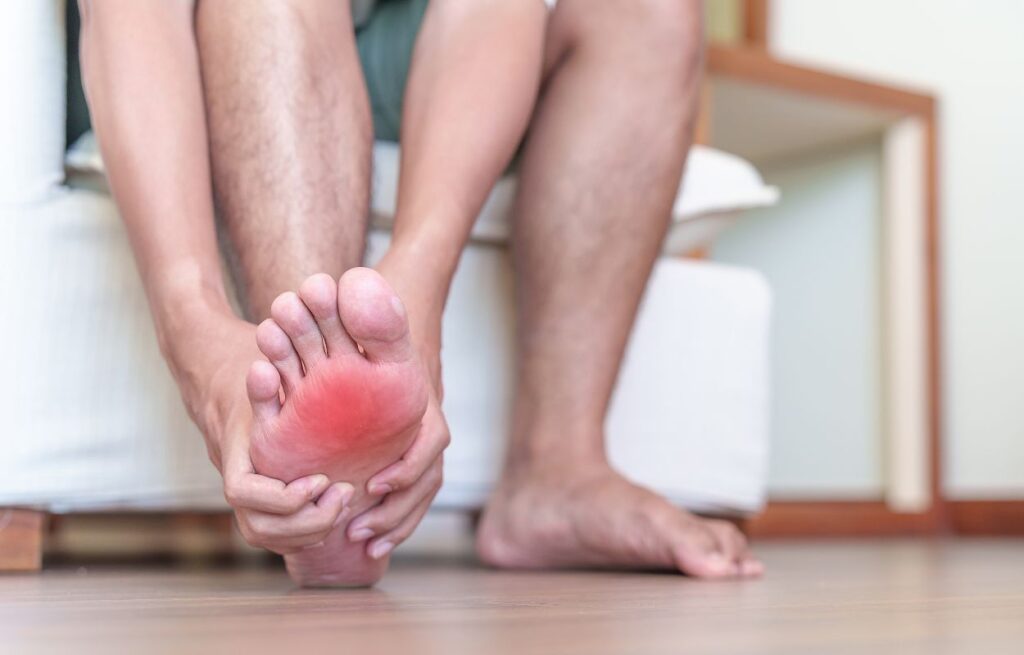
Plantar fasciitis is a condition that affects the foot’s connective tissue, specifically the plantar fascia, which extends from the heel to the base of the toes. This band of tissue plays a key role in supporting the arch of the foot and absorbing the force of daily activities. When irritation or stress occurs in the plantar fascia, individuals may experience persistent discomfort that disrupts their regular routines. Understanding the practical impact of plantar fasciitis and identifying supportive management strategies is fundamental to maintaining mobility and quality of life.
How Plantar Fasciitis Impacts Daily Activities
Plantar fasciitis affects more than foot comfort; it alters how individuals perform daily tasks and participate in social, work, and recreational activities. The condition is often noticeable during movements such as standing, walking, or transitioning from a seated to a standing position, and it can limit activity over time. Some ways this condition influences daily living include:
Discomfort During First Steps
Discomfort upon standing after rest is a key symptom associated with plantar fascia inflammation. After a period of sleep or inactivity, the plantar fascia tightens and adapts to an unloaded state. Placing weight on the foot upon rising often produces a sharp, concentrated sensation in the heel. This discomfort may linger for several minutes and tends to subside as the tissue gradually loosens with movement. The pattern can repeat throughout the day, each time there is a transition from rest to standing; this creates a cycle that challenges mobility from the start of morning routines to later periods of inactivity.
Difficulty With Standing and Walking Tasks
Activities that involve prolonged standing or continuous walking frequently become challenging for those managing plantar fasciitis. Possible scenarios include:
- Working on hard surfaces,
- Participating in retail or service roles
- Running errands
- Performing household maintenance.
Over the course of the day, the cumulative effect of bearing weight causes discomfort to intensify. It may impact a person’s ability to remain active. Adapting to these limitations is fundamental for individuals who want to maintain independence in personal care and community engagement.
What You Can Do to Manage Plantar Fasciitis
Managing plantar fascia inflammation involves adopting practical strategies designed to minimize symptoms and support routine activities. Early intervention, consistent self-care practices, and professional guidance form the basis of effective management. The following approaches help create a framework for addressing the challenges associated with the condition:
Adjust Physical Activity and Incorporate Stretches
Modifying physical activity is a helpful strategy for reducing the load placed on the plantar fascia. Transitioning from high-impact activities like running or aerobics to low-impact alternatives such as swimming or cycling can reduce strain on the feet. Introducing targeted stretching routines for the calf muscles and Achilles tendon helps foster flexibility in the supporting structures of the foot. Performing these stretches before rising in the morning, after extended sitting, and before physical activity is a supportive step in promoting foot function and reducing discomfort throughout the day.
Evaluate Lifestyle and Seek Guidance
Several factors can influence the severity and persistence of plantar fasciitis symptoms; these include footwear, work environment, and the way daily activities are organized. Contemplate making adjustments such as selecting shoes with key arch support or introducing cushioned inserts. Structuring the day to allow for alternating periods of rest and activity is another useful strategy. Consulting with a healthcare professional is helpful if discomfort persists despite these modifications.
Consult a Plantar Fasciitis Specialist
For those who continue to experience limitations despite self-care strategies, scheduling an appointment with a plantar fasciitis specialist is a key next step. Specialists evaluate the foot thoroughly and create treatment plans based on the latest clinical guidelines for heel pain. Early evaluation and intervention can help safeguard mobility, reduce disruption to daily life, and support continued participation in meaningful activities. Contact a foot specialist to enhance your daily comfort and functional independence today.